St.Venant or Pure Torsion – Pure Torsion is the in-plane twisting of a structural shape due to an applied torque. It is defined as the 1st derivative of the angle of twist “θ” pivoting about the longitudinal axis through the shear center and it varies with different end conditions. For a simply supported beam of length “L” the equation for the angle of twist “θ” due to torque “M” applied at distance “Z” from the support is shown below:
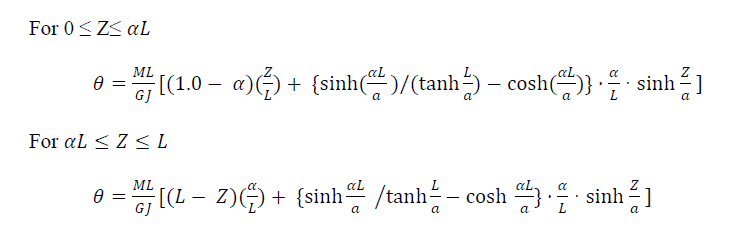
Where GJ is the material torsional rigidity and a is a torsional constant
Warping Torsion – A member having opened cross section when subject to applied torque will experience both in-plane twisting and out-of-plane warping or displace axially, which results into warping normal stresses. Warping torsion is defined based on the 2nd derivative of the angle of twist “θ”.
Warping Shear – As the cross section warps, warping shear stresses are generated as result of change in warping normal stress across the profile. Warping shear is defined as the 3rd derivative of the angle of twist “θ”.
Shear Center – The shear center is a point on a cross section where the application of load does not cause twisting.
Principal Axes (X’, Y’) – X’ is the principal strong axis about which the moment of inertia I’x is at a maximum while Y’ is the principal weak axis about which the moment of inertia I’y is at the minimum. When a member is under transverse load, the cross section tends to pivot about the principal centroid that settles the load resultant into bending about the most stable axis, the principal Y’ axis. For unsymmetrical sectioned members, such settlement can never materialize since the center of twist is taken by the shear center.
Plastic Modulus (Zx, Zy) – The plastic section modulus is the sum of the first moment of areas of the cross section of each side of the plastic neutral axis passing through the plastic centroid.
Plastic Centroid (ex, ey) – The plastic centroid is the location through which the resultant force that produces a uniform strain at failure.
Warping Constant (Cw) – The warping constant measures the resistance of a structural member owing to warping torsion.
Pure Torsion Constant (J) – The constant J measures the resistance of a structural member to Pure Torsion.
Torsion Characteristic parameter (β) Beta − calculated as the square root of GJ/ECw and is used to determine if the behavior of a cross section is controlled by Pure Torsion, Warping Torsion or Mixed Torsion (somewhere in between).
Statical Moments (Qx, Qy) – Statical moments are the first moments of inertia of an area about the principal X or Y axis, respectively.
Warping Static Moment (Sw) – The warping static moment is a constant used to calculate warping shear stress. Sw =∫ ωn da where ωn is a sectoral coordinate.
(ωn) – is a sectoral coordinate for determining the Warping Static moment(Sw).